Treatment of blood from the anus in women. Blood from the anus: when you urgently need to call an ambulance
The appearance of blood during bowel movements is a serious symptom that rarely goes unnoticed. However, when faced with such a problem, a person is in no hurry to report his concerns to the doctor, and all because he considers such a problem shameful and is simply embarrassed by doctors.
But there are incredibly many reasons for the appearance of blood from the anus, and the degree of their danger can vary from minor damage to the anal mucosa, to cancer, which can threaten a person with death. That's why this unpleasant problem You can’t ignore it and expect it to go away on its own. In this article, we will look at the reasons for the appearance of blood in the stool, and we will tell you what should be done in such a situation.
When to call an ambulance
Noticing the appearance of blood from the anus, a person immediately thinks about visiting a doctor. But in some cases, delay can threaten the patient’s life. You need to call an ambulance if:
- Heavy bleeding began from the anus, which does not stop after the completion of the bowel movement;
- the blood emerging from the anus is complemented by nosebleeds and hematomas on the body;
- bleeding is accompanied by bloody vomiting;
- the appearance of blood in the stool occurs against the background of deterioration in health;
- parallel with the appearance of blood from anus cramps occur in the abdomen and rises heat.
Causes of bleeding from the anus
Let us say right away that there are many reasons for the appearance of blood in stool. Often this symptom is caused by an exacerbation of hemorrhoids or indicates diseases gastrointestinal tract. However, infectious agents, tumors, and even injuries can cause blood to enter the rectum. internal walls intestines. Each such problem has distinctive features, to which the person caring for own health, must pay attention. Let's look at each and them.
This disease affects two thirds of people over 40 years of age and virtually every 4th person after 25 years of age. The cause of this disease is varicose veins located in the thickness of the rectum or surrounding the anus. Exacerbation of hemorrhoids causes the appearance of blood in the stool.
A person who has such a problem suffers from constipation, and during the act of defecation he feels a fragment of a swollen vein filled with blood appearing from the anus. With each act of defecation, a moderate amount of blood is released from the anus scarlet color, although as the disease progresses, bleeding can be prolonged, causing anemia and deterioration in the general condition of the body.
This problem should be solved exclusively by contacting a proctologist. After performing a digital examination and the necessary rectoscopy in this case, the doctor prescribes treatment.
First of all, doctors recommend changing your diet and eating more liquid food without causing constipation. The diet should always contain: beets, kefir, prunes, as well as all kinds of vegetables and fruits containing indigestible dietary fiber. If necessary, the patient can take mild laxatives such as Senade or Mucofalk. An effective pain reliever, as well as a remedy that can stop bleeding, are Relief suppositories and others. If drug therapy does not help cope with the existing problem, doctors use sclerotherapy or perform surgery to remove the hemorrhoid. True, it is not always possible to completely eliminate the problem in this way, because... the likelihood of relapse remains.
2. Stomach ulcer or duodenal ulcer
Ulcerative lesions of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract also often manifest themselves bloody discharge in feces. Moreover, the symptoms of these diseases depend on the size of the defect in the mucous membrane. If the defect is small, the disease may manifest itself only as pain on an empty stomach and minimal discharge of dark, clotted blood.
If the disease begins to progress, and the ulcer grows and penetrates the intestinal wall, heavy bleeding from the anus occurs, which signals a serious danger to the patient’s life. This state is complemented tarry stools and vomit streaked with blood. Having noticed the first signs of perforation of the gastric wall, you should immediately call " ambulance“, because the patient may die from excessive blood loss, or from intestinal contents entering the abdominal cavity and developing peritonitis.
Faced with such a situation, experts carry out emergency diagnostics using gastroscopy and simultaneous treatment, in which the detected defect is cauterized. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory therapy and treatment aimed at combating Helicobacter, and therefore the root cause of peptic ulcer disease.
3. Anal fissure
This sensitive issue It is no less common than hemorrhoids, but its causes are somewhat different. As a rule, people suffering from a fissure in the anal area most often experience chronic constipation. Moreover, the likelihood of rupture increases if the anal mucosa is irritated by soap or any other hygiene products.
When visiting the toilet, a person with such a problem feels cutting pains during bowel movements and detects drops of scarlet blood. The pain in this case is so severe that every visit to the toilet becomes a real test for a person. As a result, he begins to experience fear of defecation and develops psychological constipation, which only aggravates the existing problem.
A visual examination of the patient allows one to detect a rupture in the mucous membrane at the entrance to the rectum and make a diagnosis of anal fissure. To eliminate this problem, the doctor prescribes a diet for the patient that helps normalize stool. To do this, you need to diversify your diet with plant foods rich in fiber and drink enough fluids throughout the day.
From medications great help Treatment includes laxatives and ointments containing calcium channel blockers. Such drugs help relieve pain in the process of defecation, which helps to normalize stool. fast healing cracks. If conservative methods treatments do not produce results, the patient undergoes surgical correction, which allows you to eliminate sphincter spasms.
4. Varicose veins of the esophagus
Insidious varicose veins develop not only in the lower extremities or the anus. In case of circulatory disorders in the liver caused by hepatitis, cirrhosis or the appearance of tumors, pressure in other internal organs, including in the stomach, increases, which leads to the development of varicose veins.
On initial stages As the disease progresses, the patient feels heartburn, suffers from belching and heaviness in the stomach after eating. In addition, he begins to experience pain in the liver area. Over time, dark-colored stools are added to these symptoms, indicating the presence of dried blood in the stool. Moreover, after physical exertion and overeating, the patient may experience bleeding from the anus. The volume of blood loss is usually small, however, it can also cause the development of anemia. In rare cases, the patient develops severe bleeding and hematemesis.
To combat this disease, the doctor treats the liver in order to eliminate the main cause of varicose veins. To reduce damage to the esophagus, eliminate heartburn and sour belching, the patient is prescribed drugs from the group of antacids. If it is necessary to stop the bleeding, a special inflatable balloon is inserted into the patient's esophagus. IN as a last resort, if all the above methods do not give positive results, the person is surgery varicose veins of the esophagus with the creation of artificial connections between the veins in the liver.
5. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
These are quite similar pathologies with chronic course, which periodically manifest themselves as problems with the intestines and developing inflammation.
Both of these inflammatory diseases are characterized by abdominal pain (often on the lower left), as well as frequent constipation and multiple loose stools. And in the stool the patient detects blood impurities, which are rarely abundant. However, in some patients, in case of exacerbation ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease, heavy bleeding from the anus mixed with pus appears. Colonoscopy in this condition shows extensive ulcerations on the intestinal walls.
Such diseases must be treated urgently, because They often become the causes of oncology. In addition, diseases can provoke rupture of the intestinal wall and peritonitis, and this is fraught with the most tragic consequences for the patient.
The main drug in the fight against these inflammatory diseases is Prednisolone - a medicine that not only relieves inflammation, but also prevents the immune system from attacking its own intestines. In addition, the patient is prescribed medications that eliminate diarrhea, painkillers, and is also recommended dietary food, which does not irritate the walls of the stomach and normalizes stool. In some cases, surgery cannot be avoided, during which the surgeon removes part of the intestine covered with ulcers. And after surgery, you cannot do without long-term rehabilitation with the use of hormonal drugs.
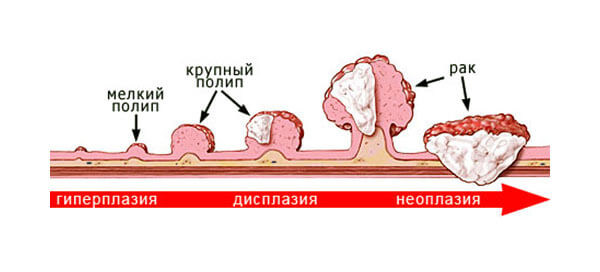
6. Intestinal polyps
In medicine, polyps are growths on the intestinal walls. It's also quite dangerous phenomenon, which often degenerates into a cancerous tumor, and therefore one should be sensitive to the symptoms that this disease manifests itself. First of all, a person’s stool becomes disrupted, constipation appears, or, conversely, he suffers from diarrhea. Moreover, the feces come out with mucus and scant admixtures of blood. Other symptoms of the appearance of polyps include pain in the intestines.
This problem is identified using colonoscopy, and it is eliminated exclusively by surgery. Moreover, given the tendency for polyps to reappear, operations will have to be repeated periodically. Moreover, each time it is necessary to conduct a histological examination of polyps, since in 30% of cases these tumors can degenerate into cancer.
Scarlet streaks in the stool indicate erosion of the vessels of the lower intestine. Any condition is dangerous to human life, so it needs to be identified at an early stage.
Causes of the problem
Blood from the anus occurs in diseases of the lower gastrointestinal tract:
- Haemorrhoids;
- Erosion of the rectum;
- Meckel's diverticulum;
- Angiodysplasia of the colon;
- Polyps of the colon mucosa;
- Intestinal inflammation;
- Radiation destruction of the epithelium;
- Tuberculous lesions of the sigmoid and rectum;
- Helminthiases.
Angiodysplasia and cavenous hemangiomas cause bleeding from the anus in 30% of cases. The severity of the condition depends on the type of angioedema:
- Type 1 – localization of formations in the colon. The size of the lesions is no more than 5 mm. Diagnosis of pathology is difficult due to the small volume of formations;
- Type 2 – large vascular lesions in the small intestine. Eliminated promptly;
- Type 3 – telangiectasia with different locations. The disease is inherited.
Diverticulosis is the cause of periodic bleeding from the anus. The frequency of detection of the disease is 16%. Despite the varying prevalence of diverticulosis painful sensations amaze left half belly. When the disease occurs, bleeding is sporadic. Reappearance occurs in 20-25% of patients.
Diverticulitis is an inflammation of Meckel's diverticulum, which is an additional extension of the intestinal mucosa into the lumen. Accession bacterial infection to pathology - the cause of vascular erosions. With pathology, streaks of blood are observed in the stool. Minor bleeding can be detected by stool analysis occult blood.
In young people, diverticulosis causes severe hemorrhages from anal passage. The pathology is complicated by polyposis. When feces pass through areas of proliferation or protrusion of the mucous membrane, they become traumatized with ulceration of the vessels. A similar situation occurs with other “plus formations” in the intestinal lumen: lymphomas, tumors, tuberculous granulomas.
The leading cause of death among patients with anal bleeding is ischemic lesions walls of the lower intestine. Embolism, thrombosis, vasculitis, atherosclerosis, abdominal trauma, radiation colitis are conditions that provoke complications of the disease.
The progression of pathology in women occurs against the background of advanced gynecological or urogenital diseases. Intestinal stones (coprolites), tumors, foreign bodies aggravate the severity of the condition.
Rupture of the aortic wall in abdominal region leads to heavy bleeding from the rectum. Situations arise spontaneously with weakness of the endothelium of an organ or after surgical interventions. No emergency medical care the disease is fatal.
Bleeding may occur with intestinal ischemia. Thrombophlebitis, embolism of mesenteric vessels, atherosclerosis are the main causes of pathology. If a pathology is detected, the doctor must rule out a rectal tumor. In elderly patients, hemorrhage from the anal canal is highly likely due to neoplasms (in the absence of hemorrhoids). Intestinal stones, vasculitis are etiological factor anemic syndrome is less common.
Profuse bleeding due to ruptures of blood vessels in the lower intestine is accompanied by the appearance of scarlet blood in the stool. This form often occurs in runners. The reason is tension in the muscles of the perineum and lower limbs, leading to compression of intestinal vessels.
There are forms of intestinal hemorrhages, the cause of which cannot be identified. The prevalence rate of nosology is about 15%.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of blood appearing from the anus against the background of increased blood pressure may be a sign hypertensive crisis. The disease is dangerous due to the rupture of blood vessels in the brain with fatal. Bleeding from the rectum is a harbinger of a serious pathology. It cannot be ignored. Careful diagnosis will prevent serious consequences in case of secondary bleeding.
Serious diagnostic value plays the color of blood. The further away the source of hemorrhage is located, the lighter blood. When the vessels of the sigmoid and rectum are damaged, a scarlet color can be seen. When varicose veins of the esophagus rupture, dark stool. It is caused by the processing of hemoglobin in red blood cells by gastric juice.
A dark red hue (“Burgundy wine”) occurs when the source is located in the proximal part of the colon. Hemorrhages due to damage small intestine manifested by hematochezia.
With cracks in the anal area, small punctate petechiae can be seen. Droplets of blood are visualized on toilet paper. The stool remains brown in color. When the source of bleeding is located distal to the rectosigmoid colon, pinpoint hemorrhages can be observed. They are clearly visualized on toilet paper by specific reddish spots.
When the source is located proximal to the rectosigmoid region, the blood mixes with the feces. With a more distal location, entire veins of scarlet blood can be traced.
These symptoms are better identified by the patient after each visit to the toilet. If abdominal pain appears with abnormal stool, this is a diagnostic symptom:
- Cutting pain syndrome– in case of aortic rupture;
- Rectal pain during stool, defecation;
- Pain with bleeding – due to intestinal infections.
Massive bleeding without attacks of pain appears with diverticulosis, telangiectasia, destruction of Meckel's diverticulum.
Other clinical symptoms of anal bleeding:
- Fever;
- Tenesmus;
- Diarrhea;
- Sweating;
- Pale skin.
Fever, joint inflammation (arthritis), erythema nodosum skin, eye iridocyclitis, cholangitis, polyarthritis, hemorrhagic vasculitis, proctitis, tenesmus are rarer signs of the disease.
Diagnostics
The following methods are used to diagnose bleeding during stool:
- Rectal digital examination;
- Fecal occult blood test;
- Anoscopy;
- Rectomanoscopy;
- Colonoscopy;
- Angiography (contrast study of the stomach);
- Scintigraphy;
- Nuclear magnetic resonance.
Establishing the source of bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract is not difficult. Colonoscopy is a probe examination of the large intestine. Difficult stool is an obstacle to the penetration of the probe into the intestine. A family history of colorectal cancer leads not only to pain in the anus, but also to bleeding. How larger sizes tumors, the more pronounced the clinical symptoms are.
Another cause of anal hemorrhage is hookworm infection. Worm infestation typical for people working on plantations, in tunnels, and mines. The pathology is characterized by telangiectasia, portal hypertension, anal fissures, hemorrhoids, villous adenomas, cancers.
To identify all of the above pathological conditions It is enough to do a sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy. Technological endoscopy helps to study in detail inner surface intestines. The examination helps to determine edema, hyperemia, granularity of the membrane, hemorrhages, pinpoint bleeding, ulcerative defects. Identification of the “cobblestone pavement” relief is characteristic of non-specific. In Crohn's disease, the large intestine is not affected, but sometimes during colonoscopy it is possible to detect areas of the mucous membrane with changes similar to this type of pathology.
Histological examination reveals abscesses and epithelioid granulomas.
For patients with ischemic colitis The mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is characterized by a bluish color. Changes may be localized in the splenic flexure, and hidden bleeding observed from the rectum.
In intestinal tuberculosis, the endoscopic picture of pseudopolyps and ulcerative defects of the gastrointestinal tract is nonspecific. Granulomas are detected only when they are in an advanced state. Specific signs of pathology are the presence of tuberculosis microbacteria, epithelioid granulomas, and multinucleated Langhans cells in the lesion.
Granulomatous radiation colitis is accompanied by changes in the mucous membrane of the large intestine, the presence of areas of ischemic necrosis, and hemorrhages.
For hemorrhages with diverticulosis, endoscopic examination reveals signs of active inflammatory process: increase in blood leukocytes, dead epithelial cells.
Bleeding from upper sections gastrointestinal tract are characterized by the appearance of occult blood in the stool. At normal stool a person does not discover on his own pathological changes health. If the source cannot be identified gastrointestinal hemorrhage, you can use selective angiography and scintigraphy.
Angiography allows you to fill the basin of the inferior and superior mesenteric arteries. Output of contrast from blood vessels into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract allows you to clearly study internal state intestinal walls.
The method is useful in the presence of angiodysplasia and diverticulosis. Positive results research obtained from clinical experiments at 60-85%.
In case of a complicated condition, scintigraphy is used - marking red blood cells or platelets with technetium pertechnetate. After a substance enters the intestinal lumen, the spectrum of its accumulation can be studied using gamma detectors.
The method is not widely used due to its complexity, duration and radiation exposure to the patient. There are modern and harmless diagnostic methods intestinal pathology(ultrasound, MRI).
Ultrasonography can be used for a thorough diagnosis. Ultrasound clearly visualizes organic formations. At cancerous tumors The method is the first opportunity for a screening examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
The use of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed only for a more thorough study of the pathological area.
Thrombophlebitis as a cause of anal bleeding
Thrombophlebitis – common reason anal bleeding in older people. Symptoms of the disease depend on the location and extent of the pathological process. The following are distinguished: clinical forms diseases:
- Superficial;
- Deep.
Thrombosis of superficial veins is characterized by local pain. The nosology is often localized in the lower leg area. Clinical symptoms superficial thrombophlebitis:
- Dense contour of the dilated vessel;
- Acute pain along the affected vessel;
- Increased pain on palpation;
- Limb movement disorders;
- Inflammation of surrounding tissues – periphlebitis.
The disease is prone to progression. In case of defeat venous vessels rectum, blood clots form bleeding. The gradual development of the disease leads to increased severity of hemorrhage. In the initial stages, the disease may manifest itself as hidden blood in the stool during stool. Over time, when defecating, a person notices scarlet blood. Pay close attention to intestinal problems. Early diagnosis saves lives.
Anal bleeding can be serious, threatening for the health and sometimes even the life of the patient. Therefore, neither the patient nor the doctor can ignore such a formidable symptom, in order to prevent further development of the disease and its complications.
Anal bleeding is an important symptom
The sudden spontaneous disappearance of bleeding from the anus is not a reason for peace, since this is a temporary condition before a re-exacerbation of the disease. But this quiet time can complicate treatment or make a positive outcome of the disease impossible.
By color bloody discharge it is possible to draw a preliminary conclusion about their origin. Bleeding can occur from any part digestive tract, and the higher the organ is located (esophagus), the darker the color of the blood will be.
This fact is explained by the influence digestive enzymes to hemoglobin in red blood cells, which changes the color of the blood from scarlet to dark brown or black. An exception to this rule may be the presence of a symptom such as diarrhea, in which the blood released into the intestinal lumen does not have time to darken due to its accelerated passage.
Main causes of gastrointestinal bleeding
Dilatation of hemorrhoidal veins of the rectum
The pathogenesis of the disease involves dilatation of the veins of the lower parts of the rectum, which leads to the rupture of one or more small veins and the release of blood. As a rule, bleeding occurs after defecation or physical activity; the patient notices the release of several drops of scarlet blood on the stool, underwear or toilet paper. Perhaps copious discharge blood, which may indicate a ruptured hemorrhoid.
The mechanism of bleeding in hemorrhoids is associated with mechanical damage dilated veins of the lower rectum passing through feces or as a result of increased pressure in them during straining or physical activity. Typically, such bleeding does not cause pain in the patient, but when it forms or occurs as a complication in the form of paraproctitis, pain is present during and after defecation. Less commonly, frequent hemorrhoidal bleeding can lead to the initial stages of anemia with all its manifestations.
With progression and absence adequate treatment the size of the nodes gradually increases, bringing increasing anxiety to the patient; their traumatization more often occurs, complicated by bleeding of various volumes. If you suspect the presence of hemorrhoids, you should urgently visit a proctologist, because timely treatment of the disease will prevent the development of its complications.
Rectal fissures

This disease develops due to mechanical impact dense feces on the wall of the rectum, in which a gap of varying length is formed, and as a result bleeding. The patient notices the discharge of scarlet blood immediately after defecation or during it, as well as sharp pain when feces pass through the area of the rectum with a crack.
A provoking factor for the appearance of blood from an anal fissure can also be exercise stress or straining of the patient due to constipation. Distinctive feature rectal bleeding resulting from hemorrhoids or anal fissure is that the stool is not mixed with blood and mucus, which in these conditions is insignificant.
If there is a lot of mucus in the stool mixed with blood, it can be assumed that the patient has a bleeding tumor (both malignant and benign) in the intestine.
Intestinal polyposis
A benign neoplasm that has a wide base or grows on a stalk is called. The course of the disease is often asymptomatic, less often with manifestations of impaired peristalsis in the form of constipation or diarrhea. Subsequently, the polyp begins to bleed, and the amount of bleeding depends on the size of the tumor. But the main danger of this neoplasm is its ability to degenerate into malignancy (intestinal cancer) over time.
Colon cancer
The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms: frequent urge for defecation, discomfort and pain in the intestinal area, discharge of blood mixed with feces and big amount mucus. These symptoms can appear already in the early stages of the disease.
Subsequently, pain occurs in the area of the sacrum and coccyx, constipation occurs, feces are released in small portions, and frequent heavy bleeding from the intestines. The main difference between bleeding from an intestinal neoplasm is Brown color bloody discharge that is mixed with stool and mucus, and may contain blood streaks or clots.
Intestinal diverticulosis
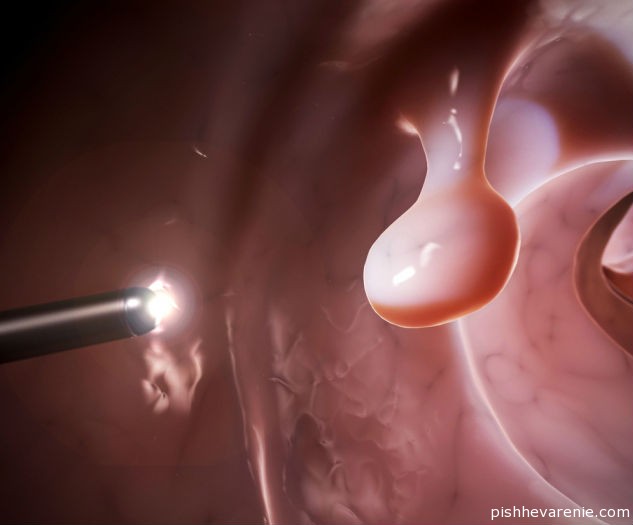
The pathogenesis of the disease lies in the weakness of the intestinal wall, in which, under the pressure arising in the intestinal lumen, protrusions and pockets are formed. Remnants of intestinal contents can accumulate in them, which leads to inflammatory changes in the diverticulum wall and its possible rupture.
The course of the disease may be asymptomatic until inflammatory changes in the diverticulum, which can manifest themselves in addition to signs of inflammation and bleeding from the intestines. Diverticulum rupture is accompanied by symptoms “ acute abdomen”: tension and sharp pain in the abdominal muscle wall, elevated body temperature, thirst and dry mouth.
When the diverticulum is localized in sigmoid region large intestine, the blood released from the intestines is scarlet in color; if the source of bleeding is located higher, the color of the blood will be black or dark brown. Since bleeding from a colonic diverticulum accompanies a violation of the integrity of its wall, in this case emergency surgical care to avoid the occurrence of life-threatening dangerous complications– peritonitis and profuse bleeding.
Angiodysplasia
This pathology occurs due to age-related degenerative-dystrophic changes in the vessels of the intestinal wall. In the intestinal mucosa, conglomerates of dilated and fragile vessels are formed, which, when ruptured, are manifested by intestinal bleeding, characterized by the release of scarlet blood from the rectum. Patients often do not notice pain with this disease, but bleeding is recurrent and chronic.
Intestinal infection
This disease is characterized by the appearance of frequent liquid bowel movements, nausea followed by vomiting or without it, manifestations of intoxication and increased body temperature. The causative agents of the disease are dysentery bacillus, salmonella, amoeba. Other conditions that may cause gastrointestinal bleeding include the following:
- and nonspecific ulcerative colitis, characterized by damage to the intestinal wall ulcerative in nature due to autoimmune pathological processes in organism. Emerging ulcerative defects of the intestinal wall lead to frequent bleeding, in addition, patients are worried about intense pain in the stomach, loss of appetite, elevated temperature bodies. The character of stool in these diseases varies from melena (black stool) to heavy bloody discharge;
- erosive colitis caused by radiation therapy;
- thrombosis of mesenteric vessels;
- ischemic damage to the intestinal wall as a consequence of disturbances in its blood supply;
- intestinal endometriosis in women during menstruation;
- damage to the intestinal wall due to helminthic infestation.
Determining the cause intestinal bleeding– the task of medical specialists who can differentiate possible diseases leading to this condition. Taking into account negative consequences in the form of malignancy benign neoplasms intestines, a visit to a proctologist should occur as early as possible, and in persons with a history of similar conditions, preferably for preventive purposes.

Anal bleeding is a reason to consult a specialist
- toilet paper for anal bleeding should have a soft and smooth structure so as not to injure the anal area, which can cause bleeding in the case of anal fissure and hemorrhoids;
- the use of toilet paper should be done with extreme caution, without unnecessary pressure on the anus, so as not to injure the area where the fissure or hemorrhoid is located;
- Untrimmed fingernails can also become a traumatic factor for the affected area.
- in addition, bleeding areas are entry points for infection and failure to comply with hygiene rules and constant trauma to the anal area threatens the occurrence of complications such as inflammation of the hemorrhoid or, which are already acute surgical pathology and require immediate intervention by a proctologist or surgeon;
- to reduce the traumatic effects of feces during defecation, it is justified to use emollients based on petroleum jelly or another similar substance, which are applied immediately before defecation to the anus;
- It would not hurt to be careful and attentive when eating, especially for people with diseases manifested by gastrointestinal bleeding, since any object that cannot be digested in the gastrointestinal tract, or even unchewed food, can become a traumatic factor and cause bleeding;
- use large quantity liquid prevents the formation of feces of a solid consistency, thereby eliminating the factor of injury when passing through the anus. The recommended minimum amount of fluid to drink is 2 liters per day.
- a positive role in reducing the factors of trauma to the anal area is played by the consumption of foods with high content fiber. To this group food products include vegetables and fruits, dishes from legumes and unground cereals. When consuming these products, the consistency of stool becomes elastic and soft, which facilitates its unhindered passage through the anus.
If, after observing all the listed precautions, bleeding from the anus has stopped, then you should still not neglect visiting a doctor, since the task of medicine is not only to eliminate the symptom, but also to find out its origin and cure its root cause, thereby preventing recurrence of bleeding.
Treatment methods for hemorrhoids

Choosing toilet paper is an important question!
In the treatment of hemorrhoids, patients should adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid constipation, especially during the period of exacerbation of the disease and the occurrence of its complications (bleeding, inflammation of the hemorrhoid). The basis for this task should be a diet high in fiber and fluid. You need to try to develop a conditioned reflex to defecate at the same time and stimulate it with fluid intake. The duration of the act of defecation should not be too long to avoid increasing pressure in the intestines. If these simple measures do not have an effect, then you should use
- conduct a daily course of local water procedures in the form of sitz baths for the anal area. They are held in evening time in cool water, which has a vasoconstrictor effect and stimulates blood supply to the anal area, or with chamomile decoction, which has disinfectant properties. The decoction is prepared from 4 tablespoons of chamomile flowers, poured into one liter cold water, by bringing it to a boil and then cooling it to room temperature;
- with the exclusion of spicy foods, coffee, strong tea, alcohol and the inclusion in the diet of a large amount of liquid (up to 2 liters per day) in the form of juices, fruit drinks, water, as well as foods rich in fiber, to form feces of soft consistency and elastic structures;
getting rid of excess weight, especially with fat deposits in the abdominal area, which are a factor that disrupts venous drainage from the large intestine; - strict adherence to hygiene rules general and the anal area in particular, which involves washing after each act of defecation with cool clean water, promoting the narrowing of blood vessels and normalizing the tone of the vascular wall;
exclude heavy lifting as a factor, causing an increase intra-abdominal and, accordingly, intra-intestinal pressure; - pay attention to moderate non-strength physical exercise for the lower body. Walking, which stimulates venous outflow from the pelvic organs, as well as gymnastics and swimming have a particularly positive effect. It is recommended to do special gymnastics for the muscles of the anal area every 2 hours, alternately tensing and relaxing them 10-15 times, as well as performing circular movements of the pelvis and bending forward and backward;
- do not use tight-fitting underwear and trousers, so as not to disrupt the venous outflow from the pelvis;
- do not take a long hot bath or shower, which increases blood flow to the pelvis and reduces venous outflow from it.
Drug treatment of hemorrhoids
The main drugs for the treatment of hemorrhoids are anti-varicose drugs that normalize blood circulation and venous outflow from the pelvic organs. Representatives of this group of drugs are troxevasin, escusan, reparil, tribenozide, anavenol, aspirin,. However, the range of their use is limited by contraindications and side effects.
Currently, searches are underway for comprehensive medicines for the treatment of hemorrhoids, since existing medicines influence a single link in the pathogenesis of the disease.
For the most curious – Bleeding from a rectal polyp. Emergency endoscopic mucosal resection:
Tell your friends! Tell your friends about this article in your favorite social network using social buttons. Thank you!
– discharge of blood from the anus due to a violation of the integrity of blood vessels in the rectum and lower parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Can be observed in a wide range of diseases of various etiologies. It appears in the form of any amount of fresh blood or clots in the stool, stains on toilet paper and underwear. Blood loss is usually minor or moderate, and heavy rectal bleeding is rare. The diagnosis is made based on symptoms, stool occult blood testing, radiological and endoscopic studies. Treatment tactics are determined by the underlying pathology.
Causes of rectal bleeding
All causes of rectal bleeding can be divided into several groups: due to benign and malignant tumors lower gastrointestinal tract, abnormal growths of the colon mucosa, chronic diseases intestines and anus, poisoning and infectious lesions, congenital and acquired disorders local circulation, stool disorders, complications various diseases and radiation therapy.
Among the oncological lesions that provoke rectal bleeding, it is primarily worth mentioning colorectal cancer. Minor bleeding with this pathology may be present already at the initial stages of the development of the disease. As the tumor disintegrates, rectal bleeding becomes more profuse, in some cases significant blood loss is possible due to the melting of a large vessel. Abnormal growths (polyps) also often cause rectal bleeding. Villous polyps, rich in blood vessels, bleed especially often.
Bleeding from the anus is constant symptom nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. In addition, rectal bleeding can be observed with diverticulitis of the large intestine, proctitis and single rectal ulcers. Sometimes minor bleeding, often detected only during a stool occult blood test, develops during normal food poisoning. This symptom also constantly occurs with infectious lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, dysentery).
Rectal bleeding is also present in pseudomembranous colitis, which occurs as a result of specific dysbacteriosis during antibiotic therapy. Sometimes in patients with bleeding from the anus, congenital vascular anomalies (angiodysplasia) or intestinal ischemia due to acquired circulatory disorders in the area are detected. abdominal cavity and small pelvis. Rectal bleeding is often caused by hemorrhoids, anal fissures and rectal prolapse.
The symptom can be observed with rectal fistulas of various etiologies (paraproctitis, Crohn's disease, diverticulitis, rectal cancer, some specific infections), intussusception and rectal prolapse. In addition, rectal bleeding often develops in cancer patients who have been prescribed radiation therapy to the pelvic area (most often for prostate cancer). Usually the symptom appears some time after completion of the course of treatment and is a consequence of radiation proctitis.
Symptoms of rectal bleeding
The nature and intensity of rectal bleeding depend on the underlying pathology. With anal fissures, patients complain of intense pain during bowel movements. Blood is separated in small quantities and is found in the form of small bright red smears on toilet paper. With hemorrhoidal rectal bleeding, similar symptoms may be observed, but there is no severe pain during defecation. Some patients experience loss hemorrhoids. The blood is often bright scarlet, although discharge is possible dark clots. Rectal bleeding with hemorrhoids is more intense, and anemia may develop.
With diverticulitis, rectal bleeding develops relatively infrequently, but can be profuse, requiring emergency treatment. therapeutic measures. The type of blood depends on the location of the diverticulum. In case of defeat sigmoid colon the blood is bright red, with diverticula of the right parts of the colon it is dark burgundy, sometimes almost black. Patients are concerned about abdominal pain, fever and hyperthermia resulting from inflammation of the mucous membrane of the diverticulum. Rectal bleeding due to diverticulitis may stop on its own and then recur after several months or even years.
Rectal bleeding with colon polyps can occur against the background of subjective well-being or abdominal pain and bowel movements. The intensity of such bleeding is usually low, but their frequent repetition can cause the development of anemia, especially with hereditary familial polyposis with the presence of a large number of villous polyps prone to bleeding.
Rectal bleeding with colorectal cancer is initially minor; blood can be detected in the stool in the form of clots or streaks. As the tumor disintegrates, the volume of blood released may increase. Along with anemia, abdominal pain and stool disorders, general manifestations cancer: weakness, weight loss, lack of appetite, hyperthermia and intoxication syndrome. Rectal bleeding with angiodysplasia is not accompanied by any symptoms. There are no abdominal pains or bowel disturbances. Anemia may develop. The color of blood in polyps and cancer depends on the location of the node. The higher the tumor is located, the darker the blood that is released. With angiodysplasia, this pattern is less pronounced; the blood often has a bright red tint.
With rectal bleeding caused by proctitis and colitis of various etiologies, abdominal pain, diarrhea and pathological impurities in the stool are observed. Along with pus and mucus, streaks of blood may be detected in the fecal matter. At severe course acute diseases and exacerbations chronic forms colitis and proctitis with severe clinical symptoms Rectal bleeding may increase, but significant blood loss is uncommon. Radiation proctitis and colitis occur with similar symptoms, in most cases, rectal bleeding stops after completing the course radiation therapy. and other studies. Differential diagnosis carried out with bleeding from other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Therapeutic tactics are determined taking into account the severity and cause of rectal bleeding. In case of heavy blood loss, emergency measures are necessary to stop the bleeding in combination with replenishment of the circulating blood volume. Infusion therapy is carried out using blood and blood substitutes. The volume of blood transfusion is determined individually. To stop rectal bleeding, local hypothermia of the affected area and therapeutic endoscopic techniques are used: diathermocoagulation, laser photocoagulation, application of hemostatic films, local administration of hemostatic drugs. If necessary, emergency surgical interventions are performed.
For minor rectal bleeding, the proctologist recommends rest and prescribes special diet. If blood loss is repeated, treatment for anemia may be necessary. In all cases, the underlying disease is treated. The prognosis depends on the volume and rate of blood loss. Most rectal bleeding is self-limiting and does not cause serious violations patient's condition. The mortality rate for rare heavy rectal bleeding ranges from 4 to 10%.
In the life of any person, a situation may arise when you have to see a doctor, for example, blood appears from the anus. If the discharge is insignificant and one-time, you should not panic right away; it is likely that there is simply a failure in digestive system(hard stool after constipation). Repeated bleeding from time to time in an adult or child indicates a serious health problem (for example, hemorrhoids, cancer, polyp, fissure).
Consultation and assistance of a competent doctor is necessary:
- If bleeding from the anus occurs suddenly, is very strong and does not stop on its own.
- At the same time, vomiting with blood clots appeared.
- There is bleeding from other organs - nasal, pulmonary, hematomas on the body.
- If it has worsened significantly general state person.
- Bleeding is accompanied by fever, chills and abdominal pain.
- If - at the same time he has diarrhea, high temperature, rash or another situation - severe abdominal pain, constipation for several days, lack of gas.
These are emergency situations that require prompt medical attention. In all other cases, it is worth making an appointment with a doctor for examination and finding out the reason why they appeared.
The main causes of bleeding from the rectum
It is worth noting that gastrointestinal bleeding– a fairly common pathology in surgical practice, its causes are diverse, the clinic and treatment differ depending on the localization of the process. The location of the source can be assumed already from appearance blood. The higher it is, the darker the blood. So, if the stomach is bleeding or duodenum, then it will be characteristic change stool color (black stool or melena). If the large intestine - the blood is mixed with feces, burgundy in color, if the source is in the rectum or anus (hemorrhoids, polyp) - the blood is fresh scarlet, found after defecation on top of feces or toilet paper.
What diseases cause bleeding from the anus more often?
Anal fissure
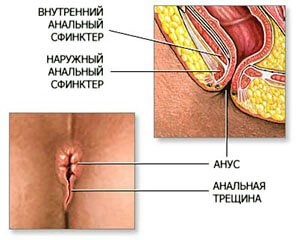 Rupture of the mucous layer of the rectum as a result of prolonged constipation, after rough anal sex, rape, accident, chronic inflammation colon. These patients are often constipated. Blood flows in a trickle after each bowel movement, and a sharp, burning pain is characteristic. Can go into chronic stage. Treatment for this pathology is only surgical.
Rupture of the mucous layer of the rectum as a result of prolonged constipation, after rough anal sex, rape, accident, chronic inflammation colon. These patients are often constipated. Blood flows in a trickle after each bowel movement, and a sharp, burning pain is characteristic. Can go into chronic stage. Treatment for this pathology is only surgical.
Haemorrhoids
IN initial stage diseases are usually small discharge scarlet blood on toilet paper, underwear, appearing after stool. In later stages, external nodes may bleed, especially with a complicated course of the disease. Worrying about thrombosis strong pain, bleeding, weakness, possible development of anemia. The disease is almost equally common in men and women (especially during and after pregnancy).
Sometimes surgery is required to stop the bleeding.
Intestinal diverticulosis
Blood from the anus is released from time to time and stops on its own; if inflammation develops, the patient is bothered by abdominal pain and fever. It is more common in men after 50 years of age. Treatment is surgical.
A coloproctologist talks about the reasons for the appearance of blood from the anus and the rules of patient behavior:
Polyp in the colon
Sometimes it bleeds very heavily, usually after a bowel movement, pain is not typical, so for a long time the patient may not be aware of its existence. Exacerbation is provoked by the appearance of constipation. Treatment is only surgical - after detection, it is necessary to perform surgery to remove the polyp due to high risk cancer development. More common in women.
Cancer
Bloody discharge, sometimes mixed with mucus and pus in the stool, diarrhea or constipation can be manifestations of cancer in the early stages, pain appears much later. Therefore, many people think that they have hemorrhoids and do not rush to see a doctor. Men are susceptible to this type of cancer more often than women. One of the most late diagnosed cancers (cause: untimely appeal on late stage process). Treatment is only radical, immediate immediately after diagnosis.
Intestinal infections – dysentery, salmonellosis
Characteristic symptoms are high fever, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and frequent urge to defecate. The stool usually contains an admixture of blood with mucus and pus. The diagnosis is made according to a characteristic clinic and after detection microbial cause in stool tests. As a result of frequent loose stool hemorrhoids may worsen. Treatment is carried out in an infectious diseases hospital.
Worm infestations
Some types of worms (amoebas, schistozomas) can damage the deep layers of the intestinal wall with the destruction of blood vessels, causing bleeding from the anus - after defecation, anal sex.
Diagnosis of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
 These two diseases are basically hereditary in nature. They are characterized by diarrhea with blood, anemia, abdominal pain, lag in physical development in children (Crohn's disease), frequent degeneration into cancer (with UC). Hemorrhoids can accompany all of the above symptoms.
These two diseases are basically hereditary in nature. They are characterized by diarrhea with blood, anemia, abdominal pain, lag in physical development in children (Crohn's disease), frequent degeneration into cancer (with UC). Hemorrhoids can accompany all of the above symptoms.
Intestinal obstruction
Severe abdominal pain, constipation for several days and “raspberry jelly” type. Treatment is carried out urgently in surgery; surgery is often necessary.
Pregnancy
 are common, the cause is almost always the same - hemorrhoids; difficulties during bowel movements due to constipation bother pregnant women from time to time.
are common, the cause is almost always the same - hemorrhoids; difficulties during bowel movements due to constipation bother pregnant women from time to time.
Severe blood (leukemia) or liver (cirrhosis) diseases
Wherein blood is flowing from the nose, uterus, lungs and other organs due to poor blood clotting.
How to deal with intestinal bleeding?

All actions of the patient should be aimed at passing full diagnostics, finding out the causes of bleeding and eliminating them:
The solution to a serious problem should not be shelved; stop the progression of the disease by early stage It is possible if you pay attention to the symptoms that appear in time.
Be attentive to yourself and your loved ones. When the first drops of blood appear from the anus, consult a doctor. In this case, you can quickly solve your health problems without any complications.





