Blueness of the skin in newborns. Acrocyanosis - how this disease is manifested and treated. Physiotherapy methods against acrocyanosis
Reducing the level of oxygen in the blood up to 92% causes cyanosis in infants. In the table, we consider the reasons that can cause this phenomenon.
Blue skin in medical terminology is called cyanosis. In fact, this is a symptom indicating a lack of oxygen in the child's body, accompanied by high content restored hemoglobin.
Prolonged rupture of membranes may indicate bacterial infection, and a history of complex delivery can lead to intracranial hemorrhage or paralysis paralysis. The physical examination should be done when the child is properly warmed up and calmed down. Growth features should be noted, as infants who are small or large for gestational age are more susceptible to polycythemia. The focus will be on determining the degree of respiratory distress, as its absence suggests the presence of congenital heart disease or methemoglobinemia.
It is what gives the skin such an atypical shade.
Types of disease
Variants of the algorithm for the development of cyanosis of the lips divide it into 3 pathological groups:
Central cyanosis is diffuse in nature and the maximum severity. It develops with weak blood arterialization, leading to hypoxia.
Respiratory failure due to lung disease is usually characterized by rapid respirations accompanied by retractions and flattening of the nose. Neurological conditions are potential causes cyanosis due to hypoventilation and may be associated with slow or irregular respirations. Exam can reveal results birth injury such as Erb's palsy or crying.
The cardiac exam should include assessment of the infant's heart rate, peripheral impulses, and perfusion. Cardiac auscultation should focus on the second heart sound, which will be loud and solitary in pulmonary hypertension, as well as transposition and atresia of the lungs. Auscultation of heart murmurs is often not helpful: severe lesions such as transposition are not associated with murmurs, and loud murmurs are often associated with relatively soft defeat such as a small ventricular septal defect.
In the lungs, gas exchange is disturbed, in arterial blood an excess of carbon dioxide accumulates, which is clinically manifested by blue conjunctiva of the eyes, palate, tongue, mucous membranes of the lips and cheeks, and facial skin.
Qualitative and quantitative changes in hemoglobin in the blood lead to a violation of its transport function and hypoxia.
A notable exception is that pulmonary stenosis is characterized by a sharp echo noise. As noted above, oxygen saturation is the percentage of hemoglobin that is chemically combined with oxygen, making up the vast majority of blood oxygen content. Pulse oximetry provides an excellent non-invasive and continuous assessment of oxygen saturation. New generation pulse oximeters appear to improve performance in low perfusion conditions. It is often useful to obtain simultaneous measurements with right hand and legs to determine patterns of flow through the ductus arteriosus.
Acrocyanosis is localized on the feet, hands, nose, ears, lips. Peripheral cyanosis is considered a normal variant in the first days of a newborn's life.
Its origin is easily explained by the incompletely eliminated germinal type of blood circulation, especially in premature babies.
The cyanosis of the skin is aggravated by swaddling, feeding, crying, and anxiety. When infant fully adapts to the outside world, cyanosis will disappear.
Since the left subclavian artery may have prior or post-collegiate aortic origin, best not to use left hand to control pulse oximetry. Although the measurement blood pressure blood oxygen oxygen is standard practice, arterial puncture pain can cause agitation and changes in ventilation and oxygenation. In any case, there is a significant metabolic acidosis may indicate heart failure, sepsis, asphyxia, or metabolic disorders.
Approaches to the diagnosis of central cyanosis
Many blood gas microanalyzers now include lactate in the measured parameters, providing additional useful information about global perfusion and oxygenation. radiograph chest is an integral part of the initial assessment of a cyanotic newborn. Examination of lung fields may reveal parenchymal lung disease or lung abnormalities such as cystic adenomatoid malformation. Elevation or hemidiaphragm by more than two intercostal spaces relative to the opposite side suggests diaphragmatic paralysis due to nerve damage.
Acrocyanosis in adults is a sign varicose veins , thrombophlebitis , vegetative-vascular dystonia , atherosclerosis, arteritis.
Cyanosis happens:
Features of treatment
To determine the exact cause of the disease, it is necessary to undergo a professional examination. Each patient has his own individual characteristics, in view of which a certain type of examination is prescribed.
Therapeutic measures in infants with cyanosis
Hyperinflated lung fields sometimes occur with emphysema of the forehead or cystic lesions of the lungs. The size and shape of the heart may provide some clues to the diagnosis: for example, "boot shape", "Tetralogy of Fallot" and the appearance of egg-on-string transposition, as well as the characteristic massive cardiomegaly of Ebstein's anomaly. chest x-ray baby with idiopathic persistent pulmonary hypertension. Pay attention to clear lung fields with reduced vascularity.
These can be various studies of the heart, lungs or blood flow.
The most common type of treatment is oxygen inhalations to enrich the blood with oxygen. Good result gives a special massage, but with chronic disease given treatment won't solve the underlying problem.

An electrocardiogram is useful for diagnosing cardiac arrhythmias. However, right-sided forces predominate in normal neonates, and mild right ventricular hypertrophy is a common finding with many types of respiratory and cardiac disease. A notable exception would be an infant with left axis deviations due to left ventricular hypertrophy, which would strongly suggest tricuspid atresia.
Some advocate the test for hyperoxia as a clinical tool to differentiate between pulmonary and cardiac disease in cyanotic children. However, the same finding may occur in infants with significant pulmonary hypertension if significant left-to-left shunting is maintained through extrapulmonary shunts.

Treatment of cyanosis is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that provoked blue skin. If the patient becomes difficult to breathe, the respiratory rate exceeds 60 breaths per minute, he sits hunched over, loses his appetite, becomes irritable and does not sleep well, you should consult a doctor.
Initial management in the emergency department
Given the wide availability of echocardiography, testing for hyperoxia is rarely necessary and should only be considered after discussion with a cardiologist. Severe cyanosis requires immediate supportive care when the diagnosis is made. This will include intravenous fluids and retention of enteral feeds. The infant should be maintained in a thermoneutral environment using radiant heat. For babies with respiratory distress respiratory and assisted ventilation should be considered, but these can be set aside for a comfortable child.
If cyanosis of the lips, palpitations, fever, cough, blue nails and difficulty breathing appear, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy can reduce the blueness of the skin. Blood oxygen saturation is achieved by using an oxygen mask or tent.
Severe acidosis should be corrected with sodium bicarbonate infusions, but only after adequate gas exchange has been established. Even short-term exposure to extreme hyperoxia is increasingly recognized to increase oxidative stress and potentially damage parenchymal and vascular function lungs, even in infants with terms. In addition, it is important to remember that oxygen can help close the ducts. However, confusional episodes such as hypoplastic left heart syndrome may present with mild cyanosis.
Prevention

Of course, in severe diseases preventive measures won't help. But if cyanosis is associated with age characteristics and the doctors confirmed its harmlessness, you can quickly get rid of it by observing simple rules:
- walk daily and a lot fresh air with a baby;
- observe the daily routine, giving enough time to sleep;
- do not overfeed the baby;
- even during pregnancy, take care of the future health of the baby, adhering to all medical advice, avoiding bad habits, stress and harmful lifestyle; this will minimize the risk of developing malformations in the fetus in the process of laying all its organs and systems.
These conditions depend on the patent duct to maintain systemic blood flow. Oxygen can not only contribute to the closure of the ducts, but can increase pulmonary and reduce systemic blood flow. The oxygen concentration should be measured with an oxygen analyzer placed near the child's mouth. Relatively high flows are required to achieve adequate oxygen concentrations and prevent accumulation carbon dioxide although hydration is usually not required. While oxygen in the headbox is generally well tolerated, this method limits the infant's mobility, and oxygen concentrations drop rapidly when the hood is raised to provide care for the infant.
IN 90% OF PEOPLE
GASTRITIS AND ULCER - IS THE SENTENCE OF THE STOMACH?
Constant or intermittent pain in the abdomen, which can be given to the left or right side. Is it sharp, aching, dull, pulling or sharp? All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
aching, nagging pain under the rib on the left may indicate the presence of a purulent-necrotic focus. The most vulnerable areas are the stomach, spleen, subcostal part.
Therefore, this method is not usually used when long-term oxygen treatment is required. Oxygen is often delivered by nasal cannula. The disadvantage of this method is that the infant takes in variable amounts of room air around the nasal cannula. Therefore, it cannot provide 100% oxygen, and the oxygen concentration in the hypopharynx will be much lower than the oxygen concentration at the cannula inlet. Both oxygen concentration and cannula flow rate will be major factors that will determine the proportion of oxygen actually delivered.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn | Competently about health on iLive
From this article you will learn: what is acrocyanosis, why it appears, and how to deal with it.
Acrocyanosis is a blue tint to the skin and mucous membranes. Lips, the tip of the nose, fingers or toes, ears, and the nasolabial triangle can become blue. This happens due to a violation of blood circulation in small vessels. The reasons for this often lie in heart disease.
Causes of Poor Circulation
Therefore, it is usually best to titrate delivery to achieve desired oxygen saturation levels, typically 90% to 95% by pulse oximetry. Other common side effects include flushing and diarrhea. There are no absolute contraindications to the onset of prostaglandin, although this may worsen pulmonary edema associated with obstruction of complete abnormal pulmonary venous return.
Baby representing branch emergency assistance with cyanosis requires urgent evaluation, diagnosis and initiation of therapy. important systemic, rational approach for the diagnosis of neonatal cyanosis. Guidance is based on clinical diagnosis and attention to hemodynamic stability, prudent oxygen administration, and referral to an appropriate inpatient hospital. Although the prognosis depends on the diagnosis, it is generally good with prompt recognition and intervention.
This symptom may or may not be dangerous, depending on the cause.
The causes of acrocyanosis are treated by a cardiologist or a cardiac surgeon. Sometimes this feature does not require treatment at all.
Six types of acrocyanosis
Depending on what provokes the blue tint of the skin, six forms of acrocyanosis are distinguished:
As a service to our clients, we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will be subject to copying, typesetting and review of the resulting evidence prior to its publication in its final form. Please note that during the production process, errors may be found that may affect the content, and all legal statements disclaimers that apply to the magazine.
Circular cyanosis can be identified as a bluish tint develops around the surrounding skin of the lips. Usually a bluish tinge is quite common in newborns because their skin structure is very thin. Therefore, the blood vessels that lie directly under the skin are clearly visible superficially.
- Central. Appears as a result of congenital or acquired, vascular diseases.
- diffuse. One of the symptoms of dysfunction of the right ventricle.
- Anesthetic. It comes from cold. Sometimes it indicates diseases, but it is also typical for healthy people.
- Spasmodic. Appears due to spasm small vessels.
- Toxic. Occurs when the body is poisoned by toxic substances.
- Idiopathic (no known cause). Does not indicate disease.
The reasons
1. Causes of central acrocyanosis
The central form develops due to an increase in the level of reduced hemoglobin (which is not connected to oxygen) in venous blood, as well as stagnation of venous blood and insufficient saturation of blood with oxygen in the pulmonary circle.
Image - Bluish discoloration around the lips. Vienna of blue color and are present around the lips just below the skin, and careful observation helps to find blue shading most of the time. Normal circulation can cause pink-red pulpy blood to circulate through the arteries.
Symptoms of circular cyanosis
Blood fluctuations decrease in the vicinity of the lips along different reasons, and the blue tint is noticeable due to the presence of veins. If this shade extends to the lips, then it needs immediate health care, because it emergency. This is a very important symptom that needs to be monitored when a bluish shed develops around the lips to ensure adequate breathing in a newborn baby.
- Anorexia or loss of appetite.
- Extraordinary noise.
- Sound with noise noise.
- Unable to move due to excessive fatigue.
The reasons for this may be:
- Congenital "blue" heart defects: stenosis (narrowing) or atresia (fusion) of the tricuspid valve, (a combination of enlargement of the right ventricle, narrowing of the pulmonary trunk and malposition of the aorta), confluence of the vena cava into left atrium, transposition of the great vessels.
- Ventricular septal defect.
- Pulmonary stenosis.
- Heart failure (it can be provoked by hypertension, atherosclerosis coronary arteries acquired heart defects).
- Chronic serious illnesses bronchi and lungs, in which breathing is disturbed.
 Causes of central acrocyanosis
Causes of central acrocyanosis 2. Causes of diffuse
The diffuse form appears when the right ventricle is disturbed.
Heart disease accompanied by cyanosis
Cyanosis directly affects skin color. Possible reasons Circular cyanosis in newborns are as follows. It can develop under the following conditions. An obstruction in the pulmonary circulation and this clinical condition associated with critical pulmonary stenosis, pulmonary atresia, and Tetralogy of Fallot. Image 3 - Spell Tet while crying or feeding.
Dissonance between arterial-ventricular connections and medical point vision is called transposition of the great arteries. congenital pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome or meconium aspiration syndrome develop due to parenchymal disease. Respiratory distress syndrome also known as respiratory distress and meconium aspiration syndrome occurs due to the mixture of meconium and amniotic fluid, breathing, meconium is present in the lungs relative to the time of delivery. The above reason mainly affects newborns, except for these following conditions usually affect.
3. Causes of anesthetic
The anesthetic variety occurs as a reaction of the body to cold (when the skin temperature drops to 15-20 degrees). It occurs in healthy people in the process of normal heat transfer. In this case, a slight cyanosis of the skin appears.
A pronounced dark blue hue at the slightest freezing can be observed with:
- infectious mononucleosis;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- leukemia.
This is due to the fact that in these diseases, cold agglutinins are formed - substances that, when the temperature drops, “stick together” red blood cells, which makes it difficult for blood circulation.
4. Causes of spasmodic
The spasmodic form is a specific reaction of the body of people with astheno-neurotic syndrome. In response to any irritant, such individuals experience a spasm of small vessels. More often this phenomenon is observed in adolescents.
5. Causes of toxic
The toxic variety of the disease develops when poisoned by substances that lead to the formation of methemoglobin or sulfagemoglobin in the blood.
6. Causes of idiopathic
The causes of idiopathic acrocyanosis are not fully understood. It is known that the blue tint of the skin appears due to spasm of arterioles (small arteries) and dilation of venules (small veins). However, the person is absolutely healthy. The idiopathic form is often characteristic of girls adolescence. This feature is often associated with hormonal changes or features of the nervous system.
Also, idiopathic acrocyanosis can be in newborns. Premature babies are especially prone to this. This is due to the fact that light and the cardiovascular system not yet adapted to life outside the mother's body. This blueness of the skin usually goes away within a few days or weeks.
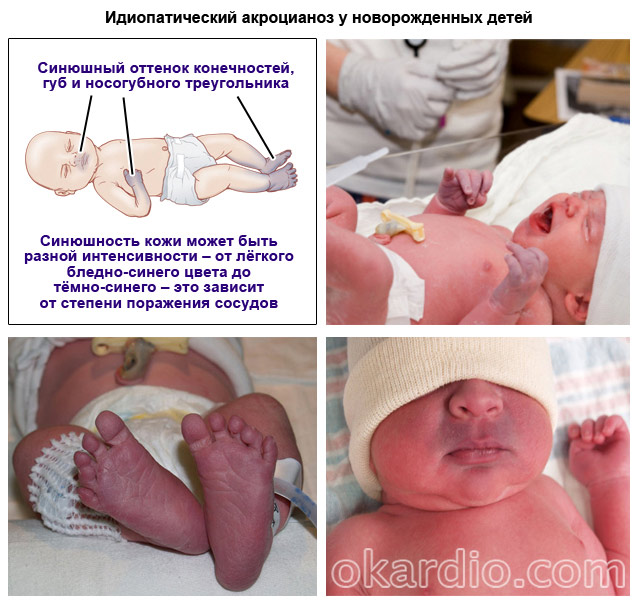
Acrocyanoses of any type are aggravated by exposure to low temperatures as well as during physical activity.
Characteristic symptoms
The disease can manifest itself as a slight bluish tint of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as a pronounced dark color. It depends on such factors:
- The severity of the disease - with "blue" birth defects and severe are the most pronounced.
- The thickness of the skin - the thicker it is, the less pronounced this symptom.
- Skin pigmentation in people with dark skin cyanosis is more difficult to detect, it can be noticeable only on the lips and on the nail plates.
- Number of small blood vessels in the skin. it idiosyncrasy. The more of them, the more pronounced acrocyanosis.
The color depends on the type of disease: with heart defects and heart failure, the skin acquires a dark blue-violet-red hue, and with lung diseases, it becomes ash-blue-gray.
Among additional symptoms acrocyanosis provoked by heart disease can be distinguished excessive sweating limbs, swelling of the affected areas.
Diagnostics
If you have noticed in yourself bluish tinge skin and mucous membranes, first of all consult a cardiologist. This may be one of the symptoms of chronic heart failure.
To diagnose it, use:
- ECG - allows you to examine electrical activity heart, its rhythm.
- EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart) - allows you to identify heart defects that could provoke heart failure.
If heart disease has not been identified, a lung and liver examination, as well as blood tests, are performed.
 Methods for diagnosing acrocyanosis
Methods for diagnosing acrocyanosis Heart defects that provoke a blue tint of the skin in children can be diagnosed even at the stage of intrauterine development during fetal echocardiography. This is very important because patients with severe congenital heart defects sometimes need to be operated on immediately after birth.
Treatment of acrocyanosis
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. With acrocyanosis of cardiac origin, any specific therapy this symptom is not carried out. Eliminate the cause that caused acrocyanosis.
Congenital and acquired heart defects require surgical correction. Sometimes they carry out drug treatment heart failure with drugs that lower blood pressure and improve myocardial performance.
If blueness is not associated with diseases, then it does not require treatment. If desired, vascular strengthening agents can be used in idiopathic acrocyanosis to avoid pathological dilatation of the venules. Such means include vitamin C, rutin, potassium and magnesium preparations. Please consult your physician before taking them.
Also, to reduce the severity of idiopathic acrocyanosis, use contrast baths for hands and feet, contrast washing, rubbing the affected areas with camphor oil.
To relieve spasm of arterioles, you can drink a course of one of these natural remedies:
- St. John's wort;
- immortelle;
- chamomile;
- Birch buds.
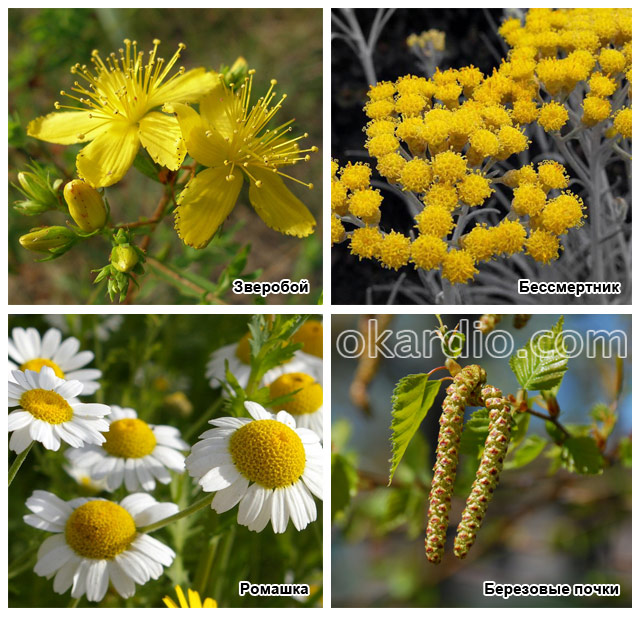 Herbs to relieve spasm of arterioles
Herbs to relieve spasm of arterioles Consume plants in the form of a decoction or tea.
Before using them, consult a therapist and carefully read the instructions if you buy herbs in a pharmacy.
Forecast
It depends on the disease that caused acrocyanosis.
With congenital malformations of the blue type, the prognosis is unfavorable. If the patient is not operated on soon after birth, a violation of the structure of the heart leads to lethal outcome.
Heart failure in the absence proper treatment also leads to grave consequences(violation of the liver, kidneys, lungs) and death. However, with the timely elimination of the cause (with the help of continuous medication or surgery), the patient returns to normal life.
With idiopathic, as well as spasmodic acrocyanosis, the prognosis is favorable. If no diseases have been identified, this condition in itself is not dangerous to health and life. But despite this, it is difficult to treat. It can be said that the idiopathic form of acrocyanosis is not medical problem but cosmetic. If the problem started during adolescence, it usually goes away with age.





